Publications
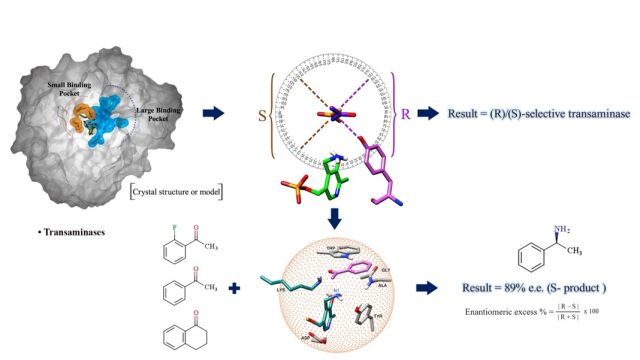 Algorithm to Predict Stereospecificity of Transaminase and its Enantiomeric Excess for a Given Substrate Using the Spatial Arrangement of Residues in the Active Site - A novel method to predict stereospecificity of Transaminases using spatial arrangement of residues in the active site and algorithm to predict ee% of transaminases for any given substrate. The study provides information on the molecular basis for engineering enzyme’s stereospecificity and a screening tool to derive focused libraries. (Under Review)
Algorithm to Predict Stereospecificity of Transaminase and its Enantiomeric Excess for a Given Substrate Using the Spatial Arrangement of Residues in the Active Site - A novel method to predict stereospecificity of Transaminases using spatial arrangement of residues in the active site and algorithm to predict ee% of transaminases for any given substrate. The study provides information on the molecular basis for engineering enzyme’s stereospecificity and a screening tool to derive focused libraries. (Under Review)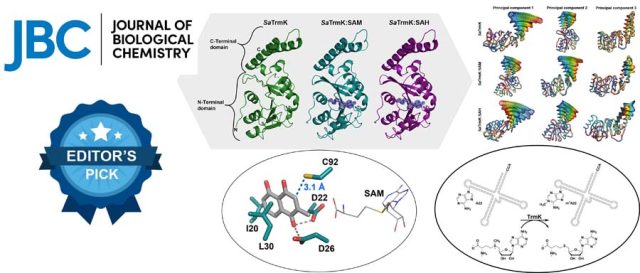 Structure, dynamics, and molecular inhibition of the Staphylococcus aureus m1A22-tRNA methyltransferase TrmK - The enzyme m1A22-tRNA methyltransferase (TrmK) from Staphylococcus aureus catalyzes the transfer of a methyl group to the N1 of adenine 22 in bacterial tRNAs. TrmK is essential for S. aureus survival during infection, but has no homolog in mammals, making it a promising target for antibiotic development. Highlights Molecular dynamics simulations point to specific motions...
Structure, dynamics, and molecular inhibition of the Staphylococcus aureus m1A22-tRNA methyltransferase TrmK - The enzyme m1A22-tRNA methyltransferase (TrmK) from Staphylococcus aureus catalyzes the transfer of a methyl group to the N1 of adenine 22 in bacterial tRNAs. TrmK is essential for S. aureus survival during infection, but has no homolog in mammals, making it a promising target for antibiotic development. Highlights Molecular dynamics simulations point to specific motions...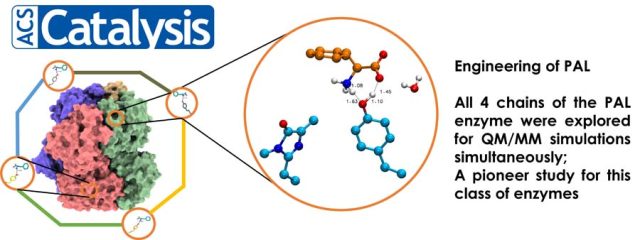 In-Depth Sequence–Function Characterization Reveals Multiple Pathways To Enhance Enzymatic Activity - Phenyl Ammonia Lyase (PAL) has garnered significant attention as the active ingredient in Pegvaliase, the only FDA-approved drug for treating classical phenylketonuria (PKU). Highlights: Deep Mutational scanning (DMS) to derive functional hotspots Hybrid QM/MM techniques combined with meta-dynamics on all 4 active sites of the PAL tetramer simultaneously, to enhance the sampling of coordinates relevant to...
In-Depth Sequence–Function Characterization Reveals Multiple Pathways To Enhance Enzymatic Activity - Phenyl Ammonia Lyase (PAL) has garnered significant attention as the active ingredient in Pegvaliase, the only FDA-approved drug for treating classical phenylketonuria (PKU). Highlights: Deep Mutational scanning (DMS) to derive functional hotspots Hybrid QM/MM techniques combined with meta-dynamics on all 4 active sites of the PAL tetramer simultaneously, to enhance the sampling of coordinates relevant to...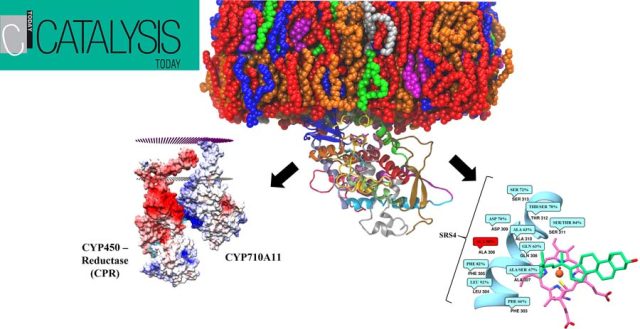 Extensive Modelling and Quantum Chemical Study of Sterol C-22 Desaturase mechanism: a commercially important Cytochrome P450 family - In this study, we have conducted in-depth modelling studies, extended molecular dynamics experiments, and quantum chemical calculations to throw light on the structure-function relationship and its mechanism of enzyme action. A novel finding on second hydrogen abstraction in the C-22 desaturase mechanism was delineated. Read More: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2021.12.004
Extensive Modelling and Quantum Chemical Study of Sterol C-22 Desaturase mechanism: a commercially important Cytochrome P450 family - In this study, we have conducted in-depth modelling studies, extended molecular dynamics experiments, and quantum chemical calculations to throw light on the structure-function relationship and its mechanism of enzyme action. A novel finding on second hydrogen abstraction in the C-22 desaturase mechanism was delineated. Read More: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2021.12.004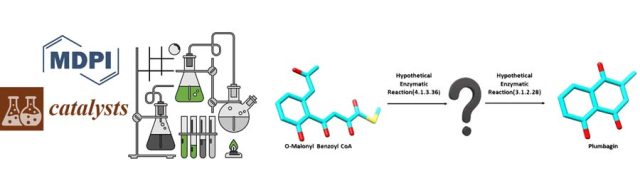 Identification of a Reaction Intermediate and Mechanism of Action of Intermediary Enzymes in Plumbagin Biosynthetic Pathway - Scaling up is a problem that a lot of biotechnologists find difficult, in terms of manufacturing techniques and products; that’s where we provide biocatalytic solutions at Kcat! The above schema is an intermediary reaction in the Plumbagin Biosynthetic Pathway. We at Kcat have identified two critical steps and respective enzymes in the synthesis of Plumbagin,...
Identification of a Reaction Intermediate and Mechanism of Action of Intermediary Enzymes in Plumbagin Biosynthetic Pathway - Scaling up is a problem that a lot of biotechnologists find difficult, in terms of manufacturing techniques and products; that’s where we provide biocatalytic solutions at Kcat! The above schema is an intermediary reaction in the Plumbagin Biosynthetic Pathway. We at Kcat have identified two critical steps and respective enzymes in the synthesis of Plumbagin,... “In Silico Based Engineering Approach to Improve Transaminases for the Conversion of Bulky Substrates” - For more information, refer to https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.8b03900
“In Silico Based Engineering Approach to Improve Transaminases for the Conversion of Bulky Substrates” - For more information, refer to https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.8b03900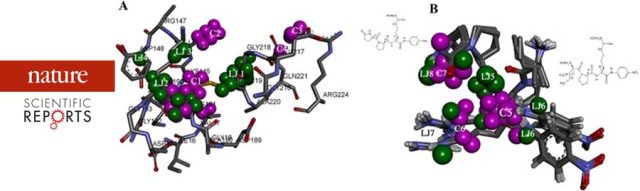 A Receptor Dependent-4D QSAR Approach to Predict the Activity of Mutated Enzymes - Screening and selection tools to obtain focused libraries play a key role in successfully engineering enzymes of desired qualities. The quality of screening depends on efficient assays; however, a focused library generated with a priori information plays a major role in effectively identifying the right enzyme. As a proof of concept, for the first time,...
A Receptor Dependent-4D QSAR Approach to Predict the Activity of Mutated Enzymes - Screening and selection tools to obtain focused libraries play a key role in successfully engineering enzymes of desired qualities. The quality of screening depends on efficient assays; however, a focused library generated with a priori information plays a major role in effectively identifying the right enzyme. As a proof of concept, for the first time,...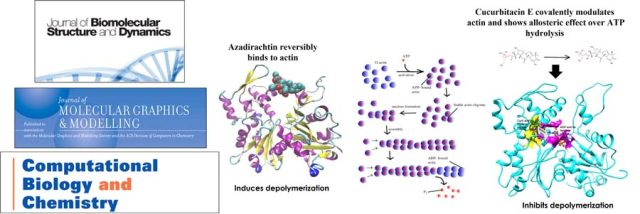 Mechanism of Phytochemicals : Affects the Polymerization and Depolymerisation of Actins - Mechanical understanding of the correlation between actin assembly and ATP hydrolysis has been an object of intensive studies in biochemistry and structural biology. Azadirachtin(A) (AZA), a potential insecticide from neem, binds to actin and induces depolymerization in Drosophila. AZA binds to the pocket the same as that of Latrunculin A (LAT), but LAT inhibits actin...
Mechanism of Phytochemicals : Affects the Polymerization and Depolymerisation of Actins - Mechanical understanding of the correlation between actin assembly and ATP hydrolysis has been an object of intensive studies in biochemistry and structural biology. Azadirachtin(A) (AZA), a potential insecticide from neem, binds to actin and induces depolymerization in Drosophila. AZA binds to the pocket the same as that of Latrunculin A (LAT), but LAT inhibits actin...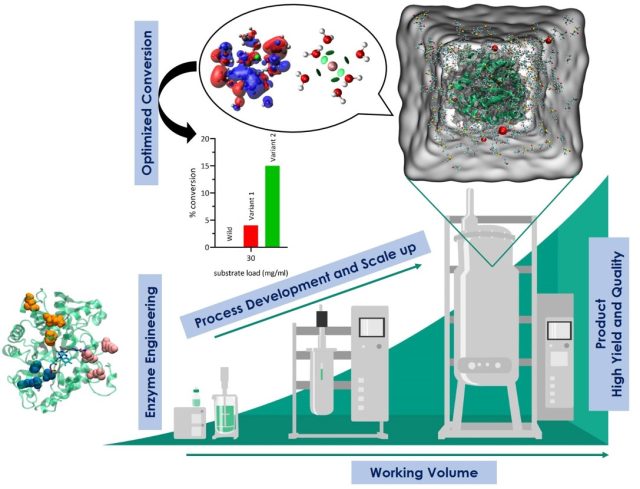 Engineering Enzymes for Improved Activity at Varying Concentrations of Substrate and Organic Solvent - One of the major problems in the use of enzymes in the industry is their instability under strict process conditions. As the use of organic solvents in industries for hydrophobic substrate solubility or the suppression of water-dependent reactions has become inevitable, the need to engineer enzymes to accommodate the varying solvent conditions and high substrate...
Engineering Enzymes for Improved Activity at Varying Concentrations of Substrate and Organic Solvent - One of the major problems in the use of enzymes in the industry is their instability under strict process conditions. As the use of organic solvents in industries for hydrophobic substrate solubility or the suppression of water-dependent reactions has become inevitable, the need to engineer enzymes to accommodate the varying solvent conditions and high substrate...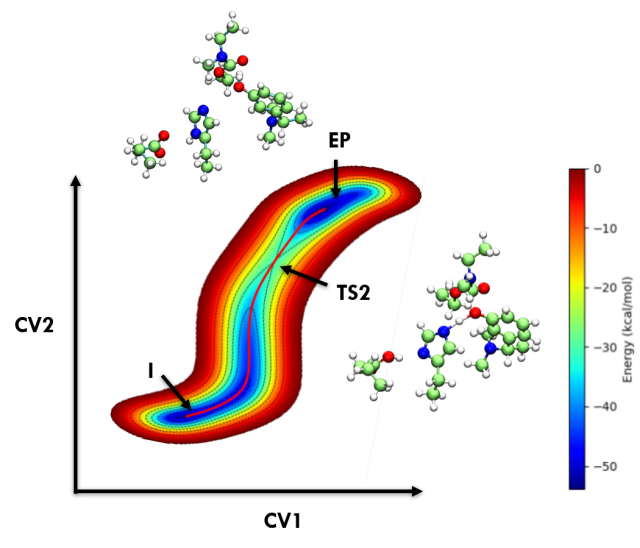 Insight Into Cholinesterase Inhibitors Mechanism By Car–Parrinello Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics In Conjunction With Metadynamics - The current study demonstrates the significant progress made in computational enzymology and exemplifies the power and advantages of employing CPMD simulations in characterizing enzyme mechanisms. Here Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors such as Rivastigmine, Physostigmine, Neostigmine, and Edrophonium binding mechanisms were explored through the metadynamics approach. (In Preparation)
Insight Into Cholinesterase Inhibitors Mechanism By Car–Parrinello Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics In Conjunction With Metadynamics - The current study demonstrates the significant progress made in computational enzymology and exemplifies the power and advantages of employing CPMD simulations in characterizing enzyme mechanisms. Here Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors such as Rivastigmine, Physostigmine, Neostigmine, and Edrophonium binding mechanisms were explored through the metadynamics approach. (In Preparation)