Scientific Posts
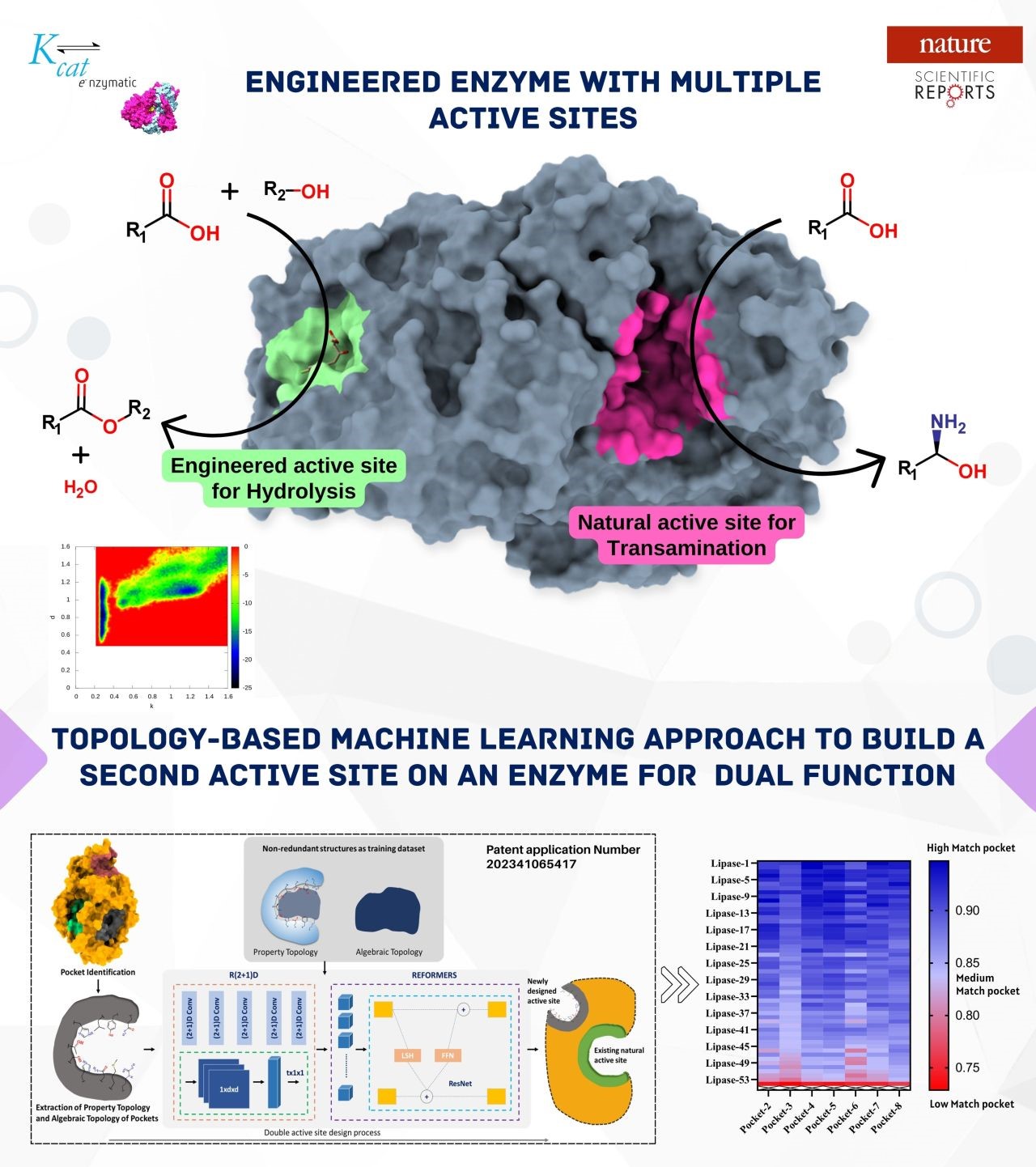 Computational studies on the catalytic potential of the double active site for enzyme engineering - We’re excited to announce our latest publication in Nature Scientific Reports on proteins with double active sites, which could revolutionize enzyme design strategies. We have developed an AI-based tool which creates enzymes with multiple active sites, enhancing their functionality by incorporating diverse catalytic activities. For example, a transaminase enzyme can now also facilitate hydrolysis reactions....
Computational studies on the catalytic potential of the double active site for enzyme engineering - We’re excited to announce our latest publication in Nature Scientific Reports on proteins with double active sites, which could revolutionize enzyme design strategies. We have developed an AI-based tool which creates enzymes with multiple active sites, enhancing their functionality by incorporating diverse catalytic activities. For example, a transaminase enzyme can now also facilitate hydrolysis reactions....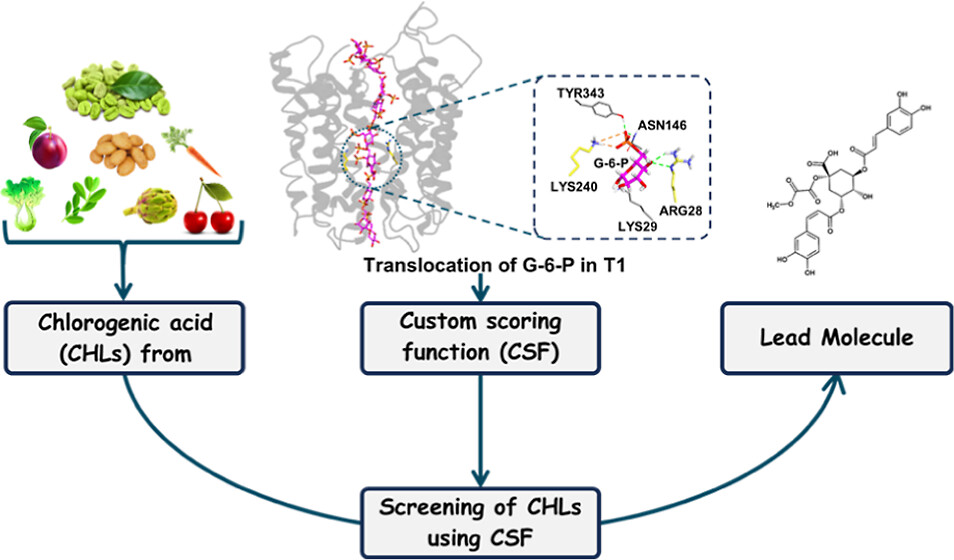 In Silico Screening of Chlorogenic Acids from Plant Sources against Human Translocase-I to Identify Competitive Inhibitors to Treat Diabetes - Chlorogenic acids (CHLs) are known to competitively bind to translocase-I (T1) of the glucose-6-phosphatase (G6 Pase) system, thereby inhibiting the transport of glucose-6-phosphate (G6P). This competitive binding results in a consequential reduction in blood sugar levels. In this study, steered molecular dynamics (SMD) simulation is employed to investigate the interaction between T1 and G6P, aiming...
In Silico Screening of Chlorogenic Acids from Plant Sources against Human Translocase-I to Identify Competitive Inhibitors to Treat Diabetes - Chlorogenic acids (CHLs) are known to competitively bind to translocase-I (T1) of the glucose-6-phosphatase (G6 Pase) system, thereby inhibiting the transport of glucose-6-phosphate (G6P). This competitive binding results in a consequential reduction in blood sugar levels. In this study, steered molecular dynamics (SMD) simulation is employed to investigate the interaction between T1 and G6P, aiming...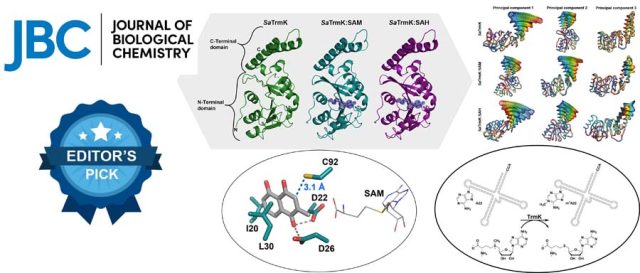 Structure, dynamics, and molecular inhibition of the Staphylococcus aureus m1A22-tRNA methyltransferase TrmK - The enzyme m1A22-tRNA methyltransferase (TrmK) from Staphylococcus aureus catalyzes the transfer of a methyl group to the N1 of adenine 22 in bacterial tRNAs. TrmK is essential for S. aureus survival during infection, but has no homolog in mammals, making it a promising target for antibiotic development. Highlights Molecular dynamics simulations point to specific motions...
Structure, dynamics, and molecular inhibition of the Staphylococcus aureus m1A22-tRNA methyltransferase TrmK - The enzyme m1A22-tRNA methyltransferase (TrmK) from Staphylococcus aureus catalyzes the transfer of a methyl group to the N1 of adenine 22 in bacterial tRNAs. TrmK is essential for S. aureus survival during infection, but has no homolog in mammals, making it a promising target for antibiotic development. Highlights Molecular dynamics simulations point to specific motions...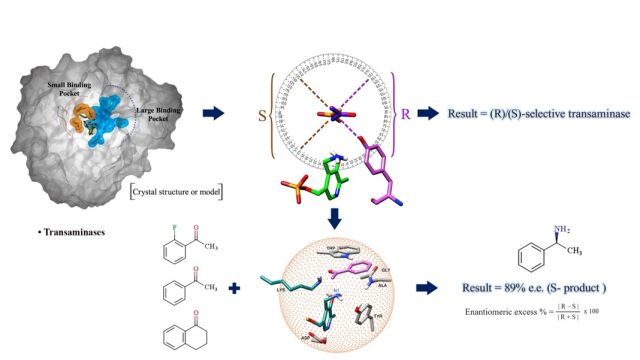 Algorithm to Predict Stereospecificity of Transaminase and its Enantiomeric Excess for a Given Substrate Using the Spatial Arrangement of Residues in the Active Site - A novel method to predict stereospecificity of Transaminases using spatial arrangement of residues in the active site and algorithm to predict ee% of transaminases for any given substrate. The study provides information on the molecular basis for engineering enzyme’s stereospecificity and a screening tool to derive focused libraries. (Under Review)
Algorithm to Predict Stereospecificity of Transaminase and its Enantiomeric Excess for a Given Substrate Using the Spatial Arrangement of Residues in the Active Site - A novel method to predict stereospecificity of Transaminases using spatial arrangement of residues in the active site and algorithm to predict ee% of transaminases for any given substrate. The study provides information on the molecular basis for engineering enzyme’s stereospecificity and a screening tool to derive focused libraries. (Under Review)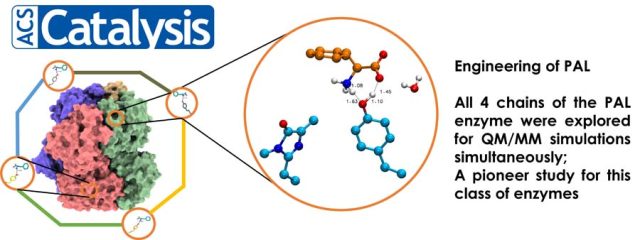 In-Depth Sequence–Function Characterization Reveals Multiple Pathways To Enhance Enzymatic Activity - Phenyl Ammonia Lyase (PAL) has garnered significant attention as the active ingredient in Pegvaliase, the only FDA-approved drug for treating classical phenylketonuria (PKU). Highlights: Deep Mutational scanning (DMS) to derive functional hotspots Hybrid QM/MM techniques combined with meta-dynamics on all 4 active sites of the PAL tetramer simultaneously, to enhance the sampling of coordinates relevant to...
In-Depth Sequence–Function Characterization Reveals Multiple Pathways To Enhance Enzymatic Activity - Phenyl Ammonia Lyase (PAL) has garnered significant attention as the active ingredient in Pegvaliase, the only FDA-approved drug for treating classical phenylketonuria (PKU). Highlights: Deep Mutational scanning (DMS) to derive functional hotspots Hybrid QM/MM techniques combined with meta-dynamics on all 4 active sites of the PAL tetramer simultaneously, to enhance the sampling of coordinates relevant to...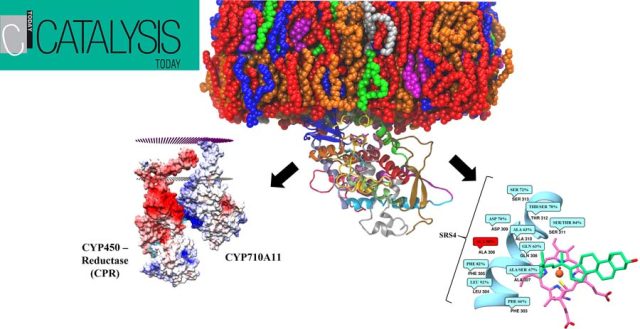 Extensive Modelling and Quantum Chemical Study of Sterol C-22 Desaturase mechanism: a commercially important Cytochrome P450 family - In this study, we have conducted in-depth modelling studies, extended molecular dynamics experiments, and quantum chemical calculations to throw light on the structure-function relationship and its mechanism of enzyme action. A novel finding on second hydrogen abstraction in the C-22 desaturase mechanism was delineated. Read More: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2021.12.004
Extensive Modelling and Quantum Chemical Study of Sterol C-22 Desaturase mechanism: a commercially important Cytochrome P450 family - In this study, we have conducted in-depth modelling studies, extended molecular dynamics experiments, and quantum chemical calculations to throw light on the structure-function relationship and its mechanism of enzyme action. A novel finding on second hydrogen abstraction in the C-22 desaturase mechanism was delineated. Read More: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2021.12.004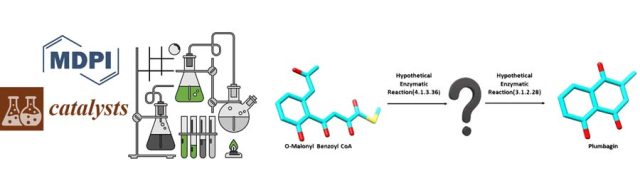 Identification of a Reaction Intermediate and Mechanism of Action of Intermediary Enzymes in Plumbagin Biosynthetic Pathway - Scaling up is a problem that a lot of biotechnologists find difficult, in terms of manufacturing techniques and products; that’s where we provide biocatalytic solutions at Kcat! The above schema is an intermediary reaction in the Plumbagin Biosynthetic Pathway. We at Kcat have identified two critical steps and respective enzymes in the synthesis of Plumbagin,...
Identification of a Reaction Intermediate and Mechanism of Action of Intermediary Enzymes in Plumbagin Biosynthetic Pathway - Scaling up is a problem that a lot of biotechnologists find difficult, in terms of manufacturing techniques and products; that’s where we provide biocatalytic solutions at Kcat! The above schema is an intermediary reaction in the Plumbagin Biosynthetic Pathway. We at Kcat have identified two critical steps and respective enzymes in the synthesis of Plumbagin,... “In Silico Based Engineering Approach to Improve Transaminases for the Conversion of Bulky Substrates” - For more information, refer to https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.8b03900
“In Silico Based Engineering Approach to Improve Transaminases for the Conversion of Bulky Substrates” - For more information, refer to https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.8b03900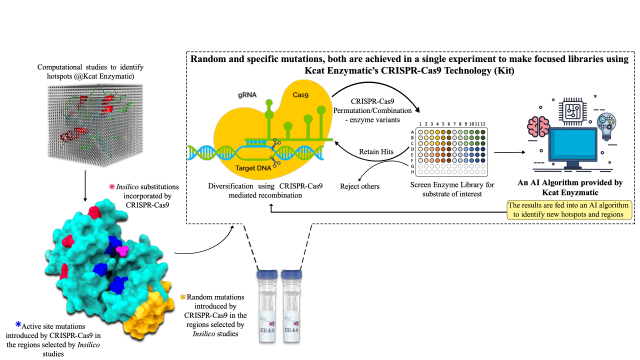 In-silico guided CRISPR-Cas9 Driven Enzyme Engineering Technology (Kit); Easy and Fast way for Engineering Enzymes - Kcat has developed a new enzyme engineering (Patent No: 202141002674, 20thJAN-21) framework with Insilico guided CRISPR-CAS driven. This framework is combined with artificial intelligence for predicting hotspots and deriving a focussed library. Salient features of Kcat Enzymatic CRISPR-Cas9 Enzyme Engineering Technology(Kit):• The source gene (enzyme) of interest will be provided by Kcat Enzymatic• The kit...
In-silico guided CRISPR-Cas9 Driven Enzyme Engineering Technology (Kit); Easy and Fast way for Engineering Enzymes - Kcat has developed a new enzyme engineering (Patent No: 202141002674, 20thJAN-21) framework with Insilico guided CRISPR-CAS driven. This framework is combined with artificial intelligence for predicting hotspots and deriving a focussed library. Salient features of Kcat Enzymatic CRISPR-Cas9 Enzyme Engineering Technology(Kit):• The source gene (enzyme) of interest will be provided by Kcat Enzymatic• The kit...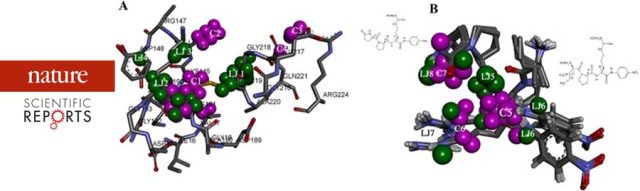 A Receptor Dependent-4D QSAR Approach to Predict the Activity of Mutated Enzymes - Screening and selection tools to obtain focused libraries play a key role in successfully engineering enzymes of desired qualities. The quality of screening depends on efficient assays; however, a focused library generated with a priori information plays a major role in effectively identifying the right enzyme. As a proof of concept, for the first time,...
A Receptor Dependent-4D QSAR Approach to Predict the Activity of Mutated Enzymes - Screening and selection tools to obtain focused libraries play a key role in successfully engineering enzymes of desired qualities. The quality of screening depends on efficient assays; however, a focused library generated with a priori information plays a major role in effectively identifying the right enzyme. As a proof of concept, for the first time,...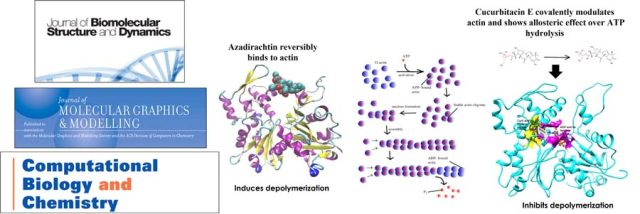 Mechanism of Phytochemicals : Affects the Polymerization and Depolymerisation of Actins - Mechanical understanding of the correlation between actin assembly and ATP hydrolysis has been an object of intensive studies in biochemistry and structural biology. Azadirachtin(A) (AZA), a potential insecticide from neem, binds to actin and induces depolymerization in Drosophila. AZA binds to the pocket the same as that of Latrunculin A (LAT), but LAT inhibits actin...
Mechanism of Phytochemicals : Affects the Polymerization and Depolymerisation of Actins - Mechanical understanding of the correlation between actin assembly and ATP hydrolysis has been an object of intensive studies in biochemistry and structural biology. Azadirachtin(A) (AZA), a potential insecticide from neem, binds to actin and induces depolymerization in Drosophila. AZA binds to the pocket the same as that of Latrunculin A (LAT), but LAT inhibits actin...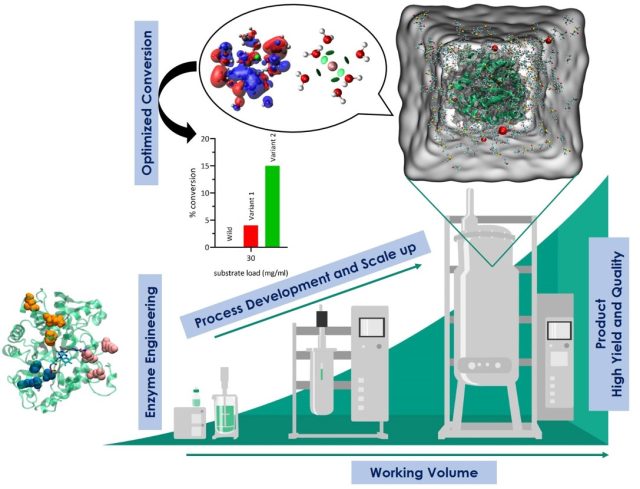 Engineering Enzymes for Improved Activity at Varying Concentrations of Substrate and Organic Solvent - One of the major problems in the use of enzymes in the industry is their instability under strict process conditions. As the use of organic solvents in industries for hydrophobic substrate solubility or the suppression of water-dependent reactions has become inevitable, the need to engineer enzymes to accommodate the varying solvent conditions and high substrate...
Engineering Enzymes for Improved Activity at Varying Concentrations of Substrate and Organic Solvent - One of the major problems in the use of enzymes in the industry is their instability under strict process conditions. As the use of organic solvents in industries for hydrophobic substrate solubility or the suppression of water-dependent reactions has become inevitable, the need to engineer enzymes to accommodate the varying solvent conditions and high substrate...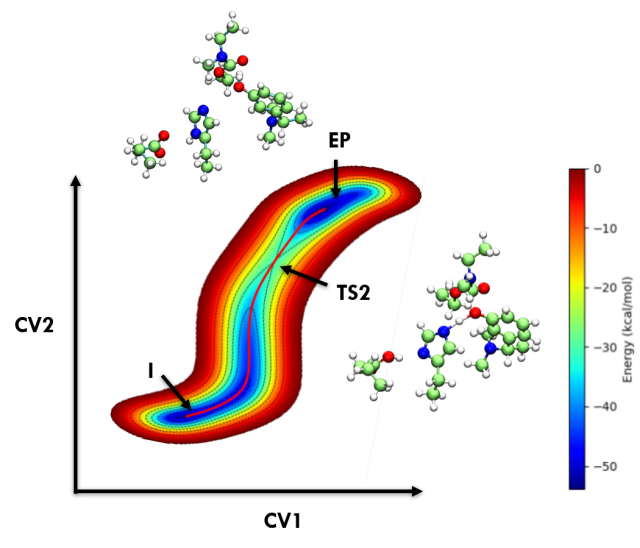 Insight Into Cholinesterase Inhibitors Mechanism By Car–Parrinello Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics In Conjunction With Metadynamics - The current study demonstrates the significant progress made in computational enzymology and exemplifies the power and advantages of employing CPMD simulations in characterizing enzyme mechanisms. Here Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors such as Rivastigmine, Physostigmine, Neostigmine, and Edrophonium binding mechanisms were explored through the metadynamics approach. (In Preparation)
Insight Into Cholinesterase Inhibitors Mechanism By Car–Parrinello Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics In Conjunction With Metadynamics - The current study demonstrates the significant progress made in computational enzymology and exemplifies the power and advantages of employing CPMD simulations in characterizing enzyme mechanisms. Here Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors such as Rivastigmine, Physostigmine, Neostigmine, and Edrophonium binding mechanisms were explored through the metadynamics approach. (In Preparation) Identification Of Hotspots And Derive Substitution For These Hotspots To Make Enzyme Variants And Screening These Enzyme Variants With Deep Learning Using A-CNN To Derive Top 5 Enzyme Variants With Desired Kinetic Property - The invention is specific to the engineering of enzymes. The Michaelis Complex of E-S reaction is simulated using QM/MM, and MD methods. Using the QM polarized grid maps, MMPBSA. MMGBSA, low energy ES conformations that lead to the formation of attack conformation are identified. Subsequently, the enzyme is designed around the Michaelis complex where the...
Identification Of Hotspots And Derive Substitution For These Hotspots To Make Enzyme Variants And Screening These Enzyme Variants With Deep Learning Using A-CNN To Derive Top 5 Enzyme Variants With Desired Kinetic Property - The invention is specific to the engineering of enzymes. The Michaelis Complex of E-S reaction is simulated using QM/MM, and MD methods. Using the QM polarized grid maps, MMPBSA. MMGBSA, low energy ES conformations that lead to the formation of attack conformation are identified. Subsequently, the enzyme is designed around the Michaelis complex where the... Swiss model becomes 25 now! - Congratulations Swissmodel for completing 25 years of service!An excellent and powerful protein modeling server, the first ever modeling server since 2002. Modeled 1000s of protein, cytoskeletal proteins like tubulin, actin, and enzymes for engineering studies like Penicillin G Acylase. A tool that can be used for teaching and as well for research purposes.
Swiss model becomes 25 now! - Congratulations Swissmodel for completing 25 years of service!An excellent and powerful protein modeling server, the first ever modeling server since 2002. Modeled 1000s of protein, cytoskeletal proteins like tubulin, actin, and enzymes for engineering studies like Penicillin G Acylase. A tool that can be used for teaching and as well for research purposes.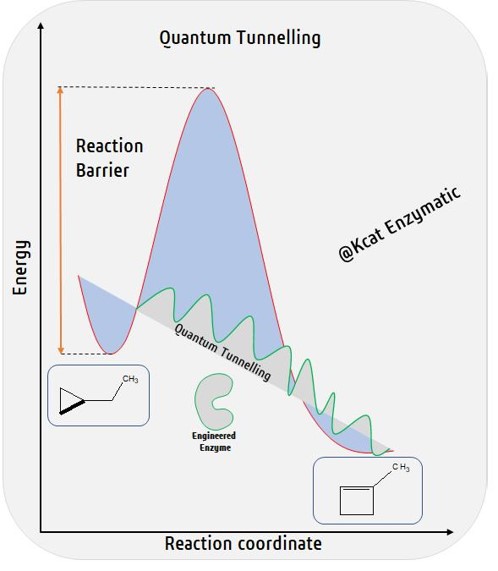 Quantum Tunnelling! - Kcat Enzymatic we are working on the similar reactions of Cytochromes as in the Nobel Laureate Dr. Arnold’s lab, however by a different technology that uses Quantum Molecular Dynamics. We wonder if enzymatic reactions take the aid of quantum tunneling effects; specifically, could it be heavy atom tunneling! A quantum mechanical phenomenon where particles penetrate...
Quantum Tunnelling! - Kcat Enzymatic we are working on the similar reactions of Cytochromes as in the Nobel Laureate Dr. Arnold’s lab, however by a different technology that uses Quantum Molecular Dynamics. We wonder if enzymatic reactions take the aid of quantum tunneling effects; specifically, could it be heavy atom tunneling! A quantum mechanical phenomenon where particles penetrate...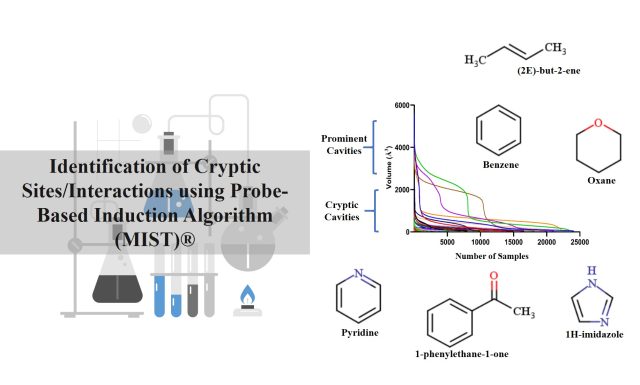 Identification of Cryptic Sites/Interactions using Probe-Based Induction Algorithm (MIST)® - Cryptic pockets are sites on enzymes that only become apparent when ligands (substrate, co-substrate, cofactor) binds. They do not correspond to local minima in the computed conformational free energy landscape of the un-liganded proteins. Hence, they close in all the molecular dynamics simulations performed. Their formation is also known to be an interplay between both...
Identification of Cryptic Sites/Interactions using Probe-Based Induction Algorithm (MIST)® - Cryptic pockets are sites on enzymes that only become apparent when ligands (substrate, co-substrate, cofactor) binds. They do not correspond to local minima in the computed conformational free energy landscape of the un-liganded proteins. Hence, they close in all the molecular dynamics simulations performed. Their formation is also known to be an interplay between both...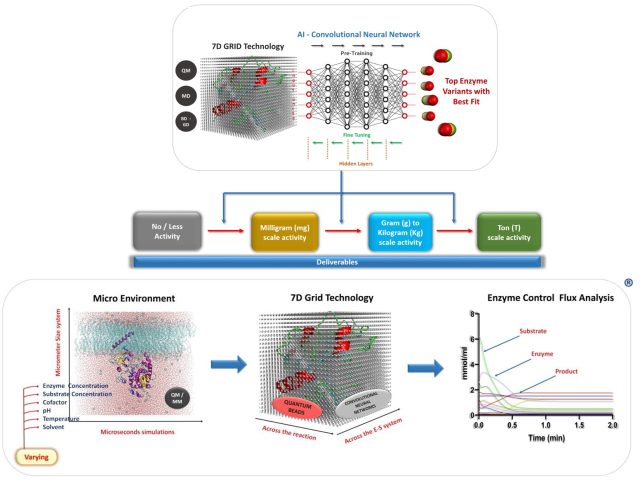 Kcat’s Technology used to derive variants to achieve kg level Substrate conversion - Schematic representation of Kcat’s Technology used to derive variants to achieve kg level substrate conversion with desired regioselectivity, stereospecificity, and enantiomeric excess. A system of Micrometer size with higher enzyme and substrate concentrations at varying pH, temperature, cofactor, co-substrate, and solvent conditions is simulated for microseconds. Information Capturing Technologies:A 7th Dimensional Grid made of Quantum beads that captures...
Kcat’s Technology used to derive variants to achieve kg level Substrate conversion - Schematic representation of Kcat’s Technology used to derive variants to achieve kg level substrate conversion with desired regioselectivity, stereospecificity, and enantiomeric excess. A system of Micrometer size with higher enzyme and substrate concentrations at varying pH, temperature, cofactor, co-substrate, and solvent conditions is simulated for microseconds. Information Capturing Technologies:A 7th Dimensional Grid made of Quantum beads that captures...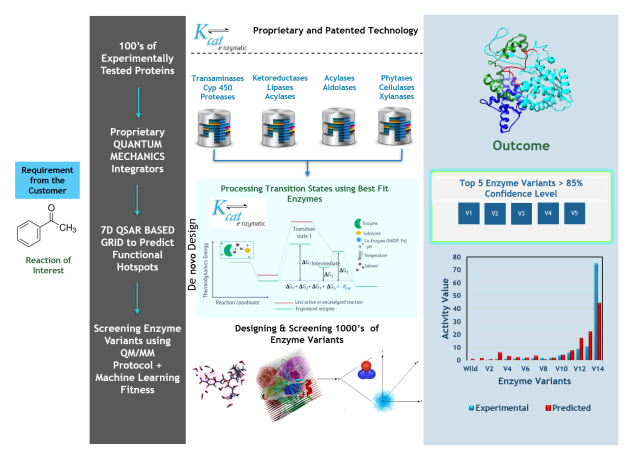 “7D-QSAR” INTEGRATED WITH QUANTUM MECHANICS A NOVEL TOOL FOR IMPROVING INDUSTRIAL ENZYMES, OUR NEW PATENT - The patented technology works on Quantum mechanics-based probes/grid points, and real solvation using semi-empirical QM simulations. The dynamic probes atoms in the grid are replaced based on the neighbor-neighbor contacts in the conformational transitions. The Dynamic grid points capture high-resolution details of the enzymatic reaction. The method was implemented on an R-specific transaminase enzyme and...
“7D-QSAR” INTEGRATED WITH QUANTUM MECHANICS A NOVEL TOOL FOR IMPROVING INDUSTRIAL ENZYMES, OUR NEW PATENT - The patented technology works on Quantum mechanics-based probes/grid points, and real solvation using semi-empirical QM simulations. The dynamic probes atoms in the grid are replaced based on the neighbor-neighbor contacts in the conformational transitions. The Dynamic grid points capture high-resolution details of the enzymatic reaction. The method was implemented on an R-specific transaminase enzyme and... To be Equipped With Weapons for Future Strains of COVID-19 - Since its first appearance in December 2019, scientists all over the world are working towards treatment for COVID-19.We are happy to announce that Kcat Enzymatic is funded by the UKRI grant for in-vitro screening and validation of molecules to target spike protein a Mpro of COVID-19. The test is being carried out at the University...
To be Equipped With Weapons for Future Strains of COVID-19 - Since its first appearance in December 2019, scientists all over the world are working towards treatment for COVID-19.We are happy to announce that Kcat Enzymatic is funded by the UKRI grant for in-vitro screening and validation of molecules to target spike protein a Mpro of COVID-19. The test is being carried out at the University... 7D GRID ENZYME ENGINEERING ENGINE® - Kcat Enzymatic brings Enzyme Engineering & Biocatalysis Revolution by using upfront in-silico in-house developed methods and algorithms using 7D Grid Technology for enzyme engineering (Patent No: 201841047021). In this line, a new and advanced way of enzyme engineering methods were developed to use enzymes in industrial processes. Our multiscale methods and technologies gives custom engineered...
7D GRID ENZYME ENGINEERING ENGINE® - Kcat Enzymatic brings Enzyme Engineering & Biocatalysis Revolution by using upfront in-silico in-house developed methods and algorithms using 7D Grid Technology for enzyme engineering (Patent No: 201841047021). In this line, a new and advanced way of enzyme engineering methods were developed to use enzymes in industrial processes. Our multiscale methods and technologies gives custom engineered...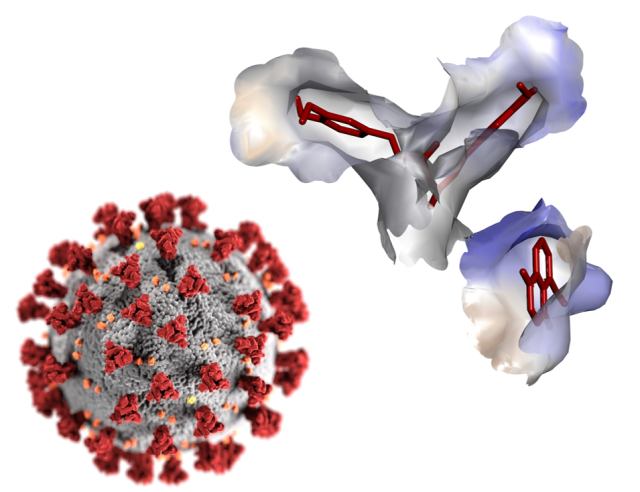 Binding Sites on Spike Protein and Cysteine Protease Mpro of Covid-19 and Identification of New Molecules Designed from Scaffolds and Pharmacophores of Phytochemicals and Synthetic Molecules that can act as Antivirals for Treatment of Covid-19 - The Coronavirus outbreak came to light on December 31, 2019 when China informed the World Health Organization. The growing COVID-19 global health crisis led us to contribute in scientific community. Kcat has contributed in identifying (Patent No: 202041038649, 08th Sep-20) antiviral compounds that can modulate the Cysteine protease Mpro and Spike protein of covid-19.
Binding Sites on Spike Protein and Cysteine Protease Mpro of Covid-19 and Identification of New Molecules Designed from Scaffolds and Pharmacophores of Phytochemicals and Synthetic Molecules that can act as Antivirals for Treatment of Covid-19 - The Coronavirus outbreak came to light on December 31, 2019 when China informed the World Health Organization. The growing COVID-19 global health crisis led us to contribute in scientific community. Kcat has contributed in identifying (Patent No: 202041038649, 08th Sep-20) antiviral compounds that can modulate the Cysteine protease Mpro and Spike protein of covid-19. Treatment for Affections of Human Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract - A plant-derived composition of active ingredients of certain plant extracts is provided to treat the affections of the Human Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract. The invention applies to healing and curative effects of certain active ingredients in the extracts of plants such as Wilbrandia ebracteate, Plumbago zeylanica, Azadirachta indica, Juglans nigra, Eucalyptus globulus, Mentha piperita,...
Treatment for Affections of Human Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract - A plant-derived composition of active ingredients of certain plant extracts is provided to treat the affections of the Human Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract. The invention applies to healing and curative effects of certain active ingredients in the extracts of plants such as Wilbrandia ebracteate, Plumbago zeylanica, Azadirachta indica, Juglans nigra, Eucalyptus globulus, Mentha piperita,... Deep Mutational Scanning Guided Directed Evolution Reveals Multiple Mechanisms to Improve Enzyme Function - This is a collaboratory work with TUFTS University, USA on the advances in Deep mutational scanning to yield hyperactive PAL variants. The reaction mechanism of the enzyme variants was confirmed through QM/MM studies combined with metadynamics. (Under Review)
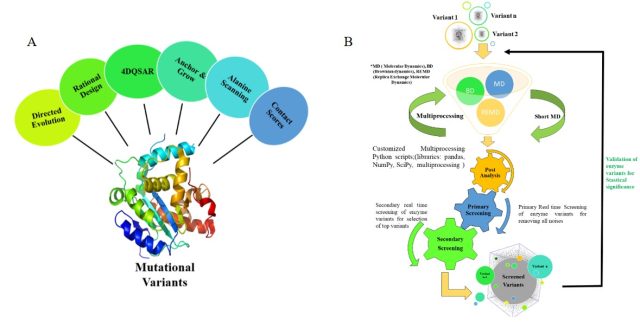 Optimizing Hardware Architecture for Screening and Selection of Enzyme Variants - Enzyme engineering is a highly sophisticated and time intensive process. In order to complement in-vitro studies and streamline the screening process for the selection of enzyme variants, in-silico analyses provide a suitable platform, as various steps can be efficiently automated with little to no burden on time and resources. In this study, we provide a...
Optimizing Hardware Architecture for Screening and Selection of Enzyme Variants - Enzyme engineering is a highly sophisticated and time intensive process. In order to complement in-vitro studies and streamline the screening process for the selection of enzyme variants, in-silico analyses provide a suitable platform, as various steps can be efficiently automated with little to no burden on time and resources. In this study, we provide a...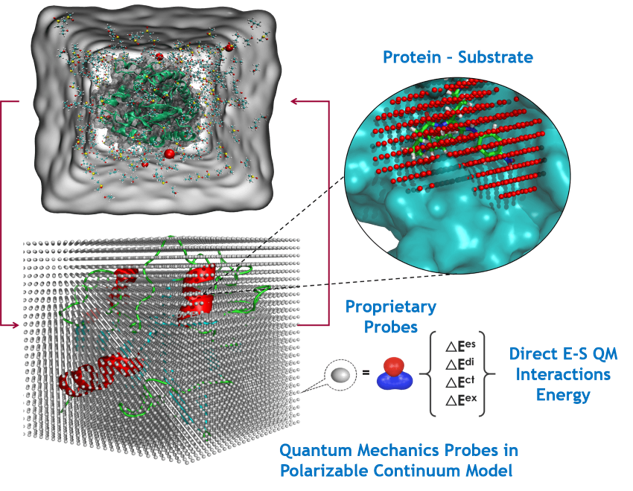 7D QSAR Based Grid Maps Generated using Quantum Mechanic Probes to Identify Hotspots and Predict Activity of Mutated Enzymes for Enzyme Engineering - 7D Grid Technology uses Quantum Mechanic probes to “capture information across the enzymatic reaction and across the enzyme-substrate system”. This information is used by AI methods, Convolutional Neural Networks, and Support Vector Machines, to design enzymes and derive focused libraries. Based on the projects done in the last 2.5 years, we can say that promiscuous...
7D QSAR Based Grid Maps Generated using Quantum Mechanic Probes to Identify Hotspots and Predict Activity of Mutated Enzymes for Enzyme Engineering - 7D Grid Technology uses Quantum Mechanic probes to “capture information across the enzymatic reaction and across the enzyme-substrate system”. This information is used by AI methods, Convolutional Neural Networks, and Support Vector Machines, to design enzymes and derive focused libraries. Based on the projects done in the last 2.5 years, we can say that promiscuous...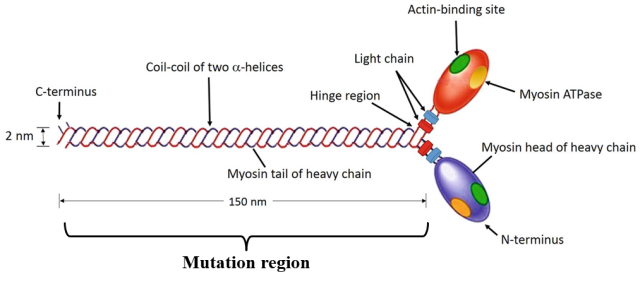 Mutations in Drosophila Myosin Rod Cause Defects in Myofibril Assembly - The indirect flight muscles (IFMs) of Drosophila melanogaster provide a good model for understanding muscle development and function in vivo. We show that two missense mutations in the rod region of the myosin heavy-chain gene, Mhc, give rise to IFM defects and abnormal myofibrils. Molecular dynamics simulations suggest that these mutations may produce localized rod...
Mutations in Drosophila Myosin Rod Cause Defects in Myofibril Assembly - The indirect flight muscles (IFMs) of Drosophila melanogaster provide a good model for understanding muscle development and function in vivo. We show that two missense mutations in the rod region of the myosin heavy-chain gene, Mhc, give rise to IFM defects and abnormal myofibrils. Molecular dynamics simulations suggest that these mutations may produce localized rod...